Software
We are eager to provide access to our results not just in form of publications, but also open source software as much as possible. Cou can find a full overview on all our software releases on our Github page.
If you have questions about any of the prototypes, feel free to get in touch. We try to maintain our code and respond to issues and pull requests as fast as we can.
Vessim
Vessim is a versatile co-simulation testbed for carbon-aware applications and systems which connects domain-specific simulators for renewable power generation and energy storage with real software and hardware.
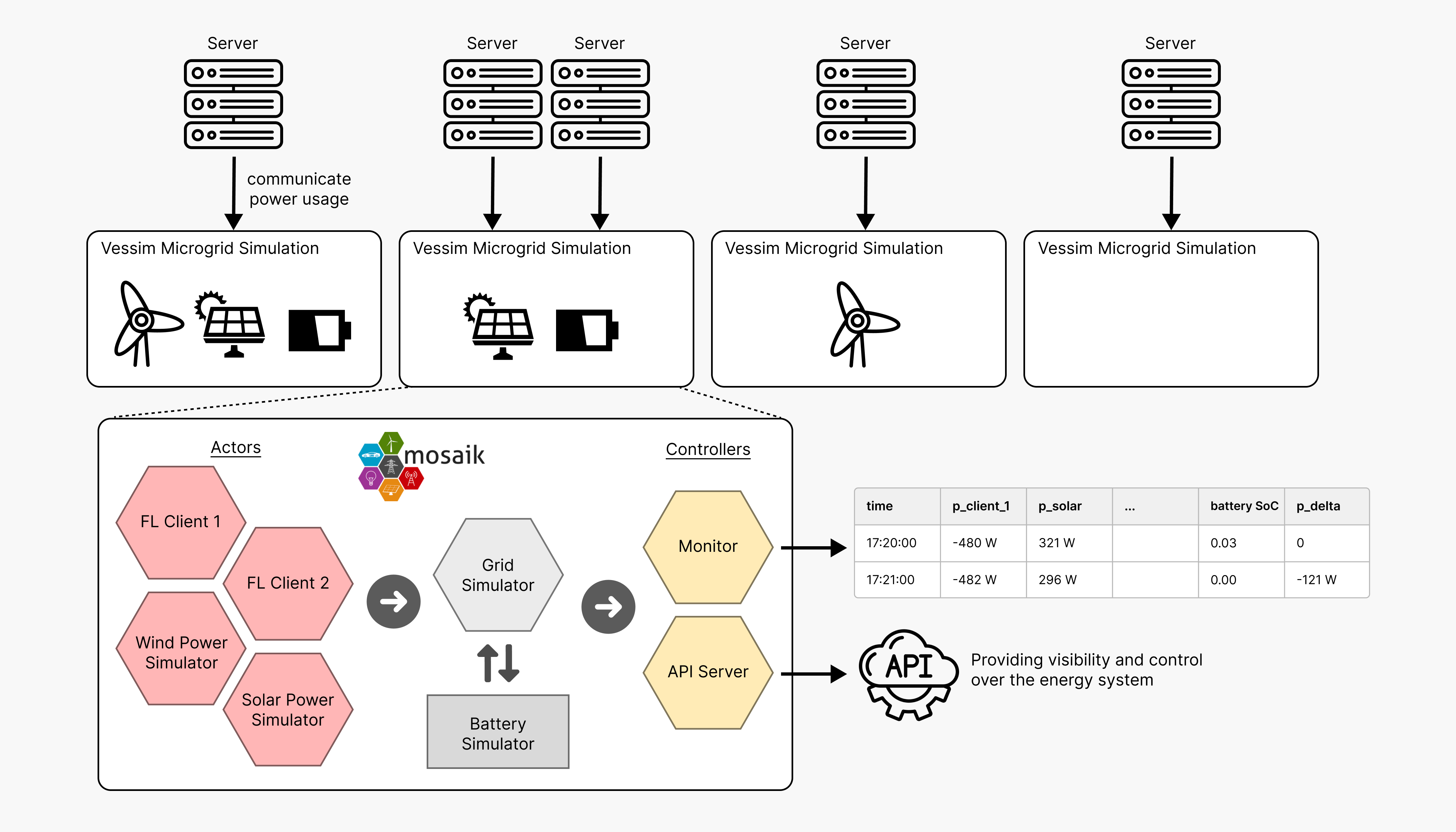
Vessim simulates energy systems that interact with real or simulated computing systems for:
- Carbon-aware applications: Microgrids simulated by Vessim offer real-time visibility and control via APIs, enabling the development and testing of novel applications that interact with their energy system.
- Energy system composition: Examine how the integration of solar panels, wind energy, or batteries would affect the energy mix of your datacenters.
- Digital Twins: Predict future system states in carbon-aware datacenters, aid decision-making, and assess risks during extreme events like power outages.
- Quality Assurance: Apply Vessim in continuous integrating testing or use it to validate software roll-outs in a controlled environment.
Github Documentation Publication
Main contact: Philipp
LEAF
LEAF is a simulator for Large Energy-Aware Fog computing environments. It enables then modeling of complex application graphs in distributed, heterogeneous, and resource-constrained infrastructures. A special emphasis was put on the modeling of energy consumption (and soon carbon emissions).
Besides allowing research on scheduling and placement algorithms on resource-constrained environments, LEAF puts a special focus on:
- Dynamic networks: Simulate mobile nodes which can join or leave the network during the simulation.
- Power consumption modeling: Model the power usage of individual compute nodes, network traffic and applications.
- Energy-aware algorithms: Implement dynamically adapting task placement strategies, routing policies, and other energy-saving mechanisms.
- Scalability: Model the execution of thousands of compute nodes and applications in magnitudes faster than real time.
Links: Github repository, documentation, and conference presentation.
Publication: LEAF: Simulating Large Energy-Aware Fog Computing Environments
Main contact: Philipp

C3O Cluster Configurator
C3O is a cluster configuration system for distributed dataflow jobs running on public clouds. It chooses a machine type and a scale-out with the goal of reaching the user’s runtime target with a certain confidence and in the most cost-efficient manner.
It contains specialized runtime models that can take the execution context (i.e. runtime-influencing job parameters and dataset characteristics) into account. Therefore it allows for the sharing of runtime data among many users with different execution contexts.
The C3O cluster configurator is implemented as a Python-based command line tool. Its repository also includes example training data, gained from 930 distinct Spark job executions
Links: Github repository with documentation
Publication: C3O: Collaborative Cluster Configuration Optimization in Public Clouds
Main contact: Jonathan Will
Water Infrastructure Monitoring Analytics Platform
We release the complete deployment code necessary to instantiate a cloud-based platform for processing monitoring data from large-scale water infrastructure monitoring campaigns. This research was conducted as part of the ongoing WaterGridSense 4.0 project and more results will be added to our repositories as the project progresses. The release includes parametrized Helm charts from which a Kubernetes cluster of arbitrary scale can be launched, as well as the code for the Apache Flink job that runs inside the cluster and enriches incoming sensor data with the required auxiliary information. The results of the data processing are published through a dedicated Apache Kafka topic, from which they can be retrieved for further processing or live visualization.
Repositories: Platform deployment charts and data enrichment job
Publication: A Scalable and Dependable Data Analytics Platform for Water Infrastructure Monitoring
Main contact: Morgan

